In the rapidly evolving landscape of Africa's economy, industrialization in Africa is not merely a goal but a vital necessity. As countries seek to navigate the challenges of underdevelopment, the question arises: what paths will lead African nations to sustainable industrial success? Join us as we explore insights from FEDA (Fund for Export Development in Africa) and examine the current state of industrialization across the continent.
Opening Inquiry: The Path to Industrialization in Africa
The path to industrialization in Africa is fraught with challenges and opportunities. With rich natural resources and youthful populations, Africa holds immense potential for industrial growth. However, understanding how to leverage these resources and transform industries is crucial.
Overview of Industrialization in Africa
Defining Industrialization and Its Importance
Industrialization refers to the process by which an economy transforms from primarily agricultural to one based on the manufacturing of goods. In the context of industrialization in Africa, this process is critical not only for economic growth but also for job creation and social upliftment. It enhances productivity and facilitates technological advancement, thereby laying the foundation for a modern economy.
Current State of Industrialization in Africa
As of now, industrialization in Africa faces significant hurdles. Many countries still depend heavily on primary commodities, which exposes them to fluctuating prices in the global market. The current state of infrastructure, regulatory environments, and access to finance further complicates industrial growth. FEDA aims to address these challenges through strategic investments and partnerships.

The Role of FEDA in Promoting Industrialization
FEDA's Mission and Objectives
FEDA is more than just a financial institution; it positions itself as a catalyst for industrialization in Africa. Its mission is designed to mobilize capital for African businesses that drive intra-African trade and value-added exports. By providing equity and quasi-equity funding, FEDA supports companies focused on manufacturing, technology, and agribusiness, aiming to bridge the investment gap across sectors.

Recent Developments and Uganda's Accession
Recent developments, such as Uganda's accession to FEDA, mark a pivotal moment in African industrialization efforts. This expansion not only increases FEDA's influence but also demonstrates Uganda’s commitment to driving economic transformation. The collaboration hopes to mobilize more resources towards fulfilling the continent's industrial ambitions. For more on how trade routes are being enhanced in the region, see MSC Revolutionizes Trade Routes: Enhanced Connectivity in Southern Africa.
Expert Insights on Industrialization in Africa
Marlene Ngoyi's Perspective on Economic Transformation
According to Marlene Ngoyi, CEO of FEDA, “Uganda’s decision to join FEDA is a testament to the country’s confidence in FEDA’s mission and to its commitment to accelerating Africa’s economic transformation...”. This statement underscores FEDA's role as a linchpin in the continent's movement towards a more industrially productive environment.

Ambassador Philip Rukikaire's Vision for a Prosperous Africa
As noted by Ambassador Philip Rukikaire, “Today marks a significant milestone in Uganda’s economic development journey. By joining FEDA, we reaffirm our dedication to a prosperous Africa...”. These insights highlight the commitment of African leaders to pursue industrialization and trade as vehicles for growth.

Benefits of Industrialization in Africa
Economic Growth and Job Creation
The benefits of industrialization in Africa are far-reaching. It not only stimulates economic growth through increased production capacity but also creates numerous job opportunities. The manufacturing sector is historically known for its ability to absorb labor, thus reducing unemployment levels significantly.

Enhancing Intra-African Trade
Another key advantage of industrialization is the enhancement of intra-African trade. By focusing on local production and manufacturing, African countries can reduce reliance on imports and foster trade relationships that are mutually beneficial. This shift towards self-sufficiency can safeguard economies against external shocks. For more insights on trade and economic strategies, explore MSC Revolutionizes Trade Routes: Enhanced Connectivity in Southern Africa.
Challenges Facing Industrialization in Africa
Infrastructure and Investment Gaps
Despite the promising prospects, industrialization in Africa is hampered by critical challenges such as insufficient infrastructure and investment gaps. Many regions lack reliable transport networks, power supply, and technological infrastructure that are essential for supporting industrial activities. This disparity needs urgent attention to realize the continent’s industrial goals.
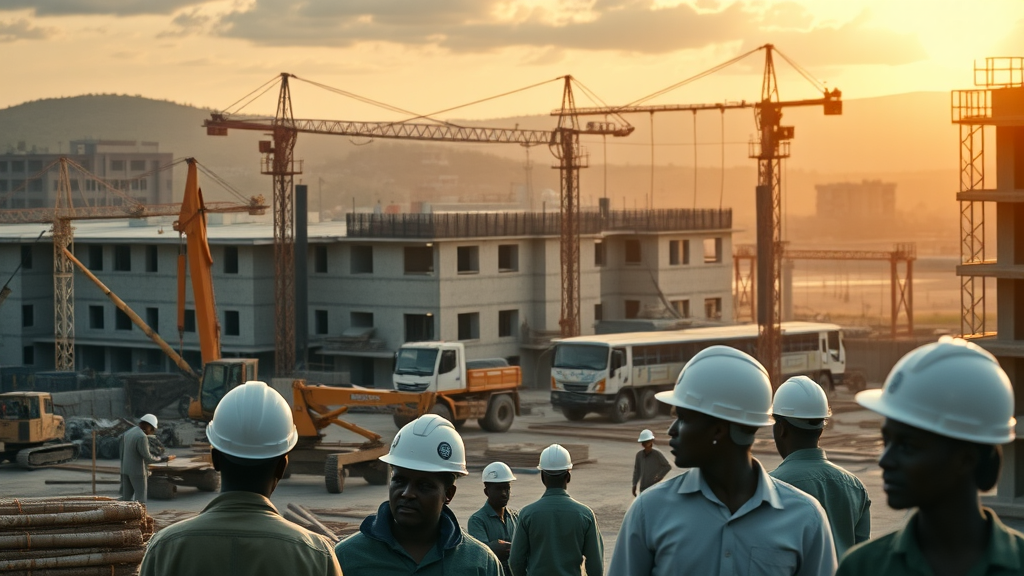

Policy and Regulatory Barriers
Additionally, policy and regulatory barriers present significant hurdles. Inconsistent regulations, high tariffs, and bureaucratic obstacles can deter both local and foreign investment. Streamlining these policies is essential for creating a conducive environment for industrial growth.
Key Takeaways on the Future of Industrialization
The Importance of Collaboration and Investment
For successful industrialization in Africa, collaboration between governments, private sectors, and international organizations is crucial. Pooling resources and expertise will magnify efforts towards sustainable growth and will effectively tackle the infrastructural and financial challenges facing the continent.
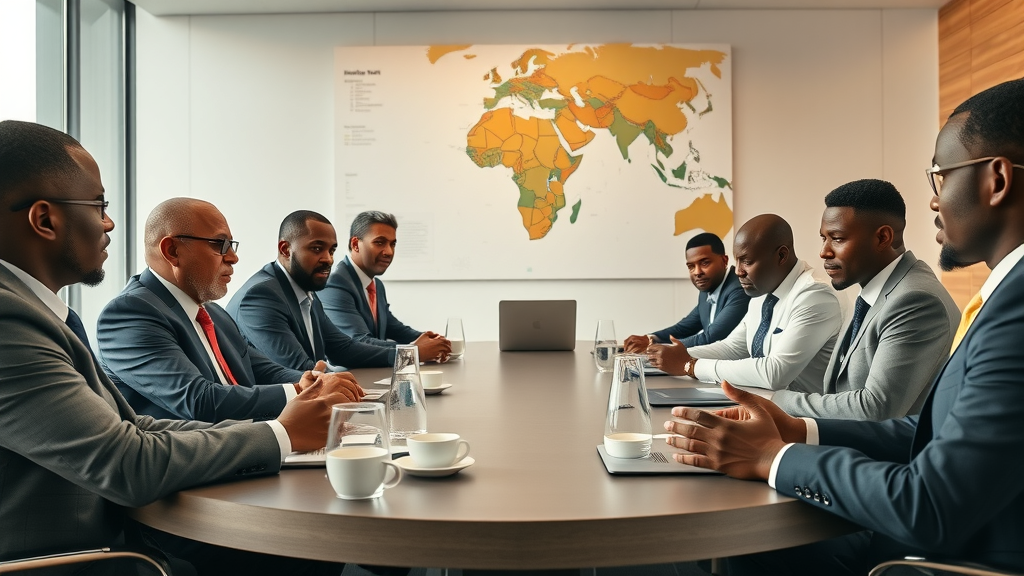

The Role of Governments and Private Sector
Both governments and the private sector have vital roles in promoting industrialization. Government policies that encourage investment, along with private initiatives that boost innovation, are necessary for building a robust manufacturing sector capable of competing globally.
People Also Ask
How did industrialization impact Africa?
Industrialization has transformed Africa by moving economies away from agricultural reliance towards manufacturing, creating jobs and reducing poverty.
What are the benefits of industrialization in Africa?
The benefits include economic growth, job creation, enhanced intra-African trade, and improved living standards.
What are the factors affecting industrialization in Africa?
Key factors include infrastructure, education, investment levels, governance, and political stability.
What countries are industrialized in Africa?
Countries like South Africa, Egypt, and Nigeria are among the most industrialized on the continent, but many others are on their path to industrialization.
Conclusion: The Path Forward for Africa's Industrialization
The future of industrialization in Africa is bright but requires strategic efforts. By fostering collaboration, addressing infrastructural challenges, and ensuring regulatory clarity, African nations can unlock their full industrial potential, driving sustainable growth across the continent.

Call to Action: Engage with FEDA and Support Industrial Growth
Interested in making a difference? Support FEDA’s initiatives aimed at driving industrialization in Africa. Engage with local industries, promote investments, and advocate for effective policies that facilitate growth.
Your browser does not support HTML5 video.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 






 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 

Write A Comment