As Africa stands on the brink of an economic revolution, the importance of intra-African trade cannot be overstated. Could it be the key to unlocking unprecedented economic growth across the continent? Join us as we explore the pivotal role of trade among African nations, the contribution of organizations like FEDA, and the strategies necessary to enhance this vital economic conduit.
What You'll Learn
- Understanding the significance of intra-African trade.
- Insights from key experts in the field.
- Strategies to overcome barriers to trade.
Opening Inquiry: The Potential of Intra-African Trade
The movement toward intra-African trade could reshape the continent’s economic landscape. With over 1.3 billion people and a combined GDP of $2.5 trillion, African countries have an immense potential market. By leveraging this potential through trade agreements and strategic partnerships, nations can increase resilience against global economic shocks and better meet the needs of their populations. With initiatives such as FEDA, the vision for trade is becoming a reality, paving the way for sustainable economic development.
Overview of Intra-African Trade
Defining Intra-African Trade
Intra-African trade refers to the exchange of goods and services between African countries. This trade encompasses various sectors, including textiles, agriculture, manufactured goods, and technology. The integration of African economies through trade is essential for fostering economic cooperation and enhancing the continent's overall growth.
Current State of Intra-African Trade
Unfortunately, intra-African trade remains frustratingly low, accounting for only about 15% of Africa's total trade. Various factors contribute to this phenomenon, including outdated infrastructure, trade barriers, and complex regulations that hinder seamless movement across borders. Despite these challenges, there is a growing recognition of the need for reforms and investments aimed at boosting intra-African trade. For instance, the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) is a significant step towards transforming logistics and trade across the continent.
The Role of FEDA in Promoting Intra-African Trade
FEDA's Mission and Objectives
The Fund for Export Development in Africa (FEDA) seeks to facilitate trade and investment throughout the continent. With objectives centered around supporting value-added export development and industrialization, FEDA plays a critical role in developing infrastructure and policies that support intra-African trade.
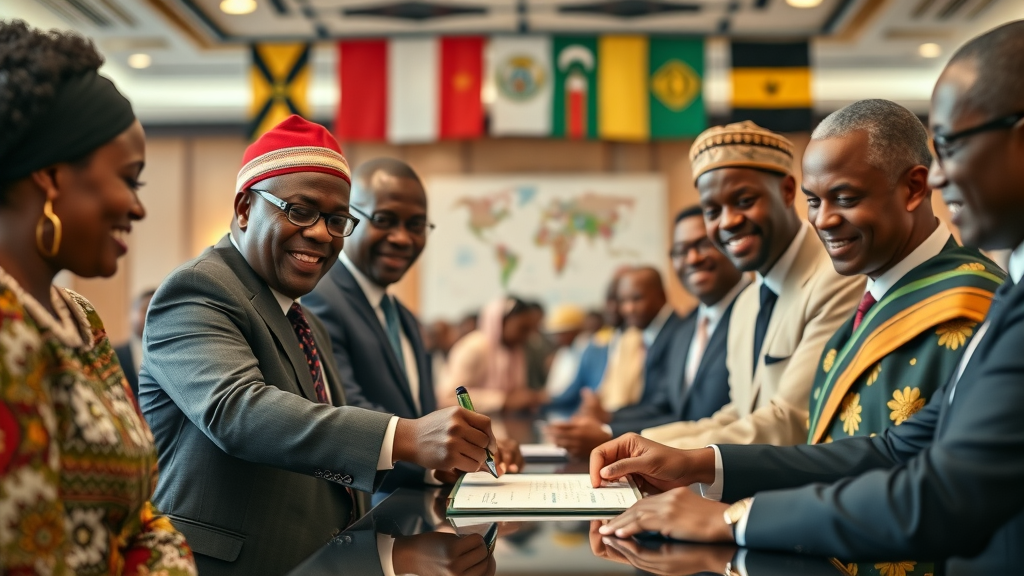
Recent Developments: Uganda's Accession to FEDA
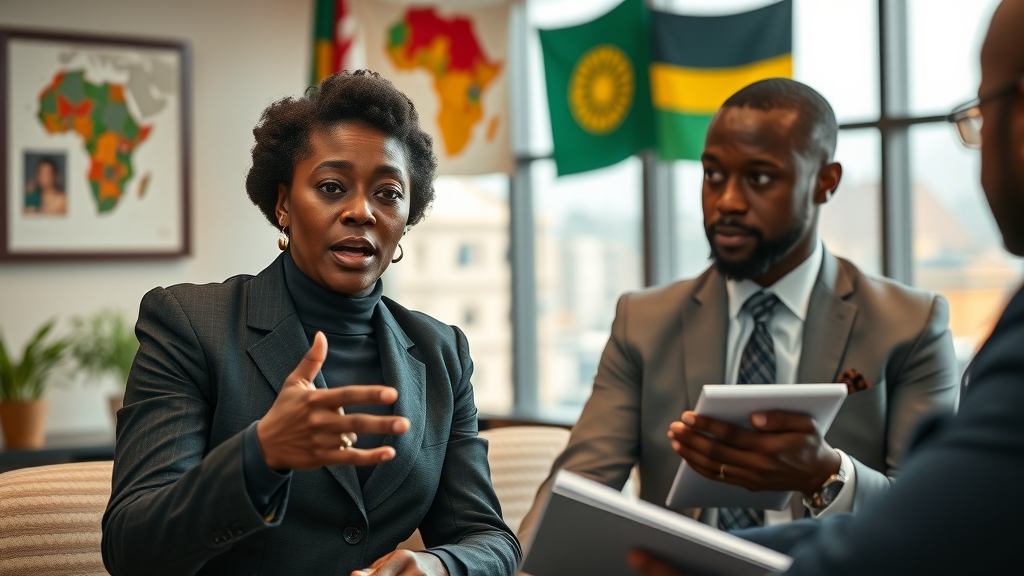
In March 2025, Uganda joined FEDA, expanding its member states to 21. This partnership is expected to significantly enhance Uganda’s economic landscape and elevate intra-African trade levels. As Marlene Ngoyi, CEO of FEDA, remarked, “Uganda’s decision to join FEDA is a testament to the country’s confidence in FEDA’s mission and to its commitment to accelerating Africa’s economic transformation…”

Expert Insights on Intra-African Trade
Marlene Ngoyi's Perspective
Marlene Ngoyi emphasizes that intra-African trade could lead to significant economic transformation. By mobilizing capital and investing in export-related sectors, nations stand a chance to unlock immense potential across Africa.
"Uganda’s decision to join FEDA is a testament to the country’s confidence in FEDA’s mission and to its commitment to accelerating Africa’s economic transformation..." - Marlene Ngoyi, CEO of FEDA
Ambassador Philip Rukikaire's Viewpoint
Ambassador Rukikaire supports the view that this partnership will provide necessary investment to propel Uganda’s manufacturing and exports. “Today marks a significant milestone in Uganda’s economic development journey. By joining FEDA, we reaffirm our dedication to a prosperous Africa…”
"Today marks a significant milestone in Uganda’s economic development journey. By joining FEDA, we reaffirm our dedication to a prosperous Africa..." - Ambassador Philip Rukikaire

Challenges Facing Intra-African Trade
Barriers to Trade
Despite its potential, intra-African trade faces numerous barriers. These include tariffs, trade restrictions, and bureaucratic inefficiencies that can discourage cross-border trade activities. Addressing these challenges is paramount to fostering a more conducive environment for trade. The DRC Port Project is an example of efforts to revolutionize trade routes and reduce such barriers.
Low Trade Volumes and Their Implications
The low volumes of trade between African nations have significant implications not only for economic growth but also for political relationships and cultural exchange. Boosting trade volumes requires serious investment in infrastructure, policy reforms, and collaborative agreements aimed at easing trade practices.

Strategies to Enhance Intra-African Trade
Investment in Infrastructure
Improving infrastructure across African nations is vital for enhancing intra-African trade. Investments in transportation networks, logistics, and communication systems can significantly reduce trade barriers and facilitate the movement of goods.
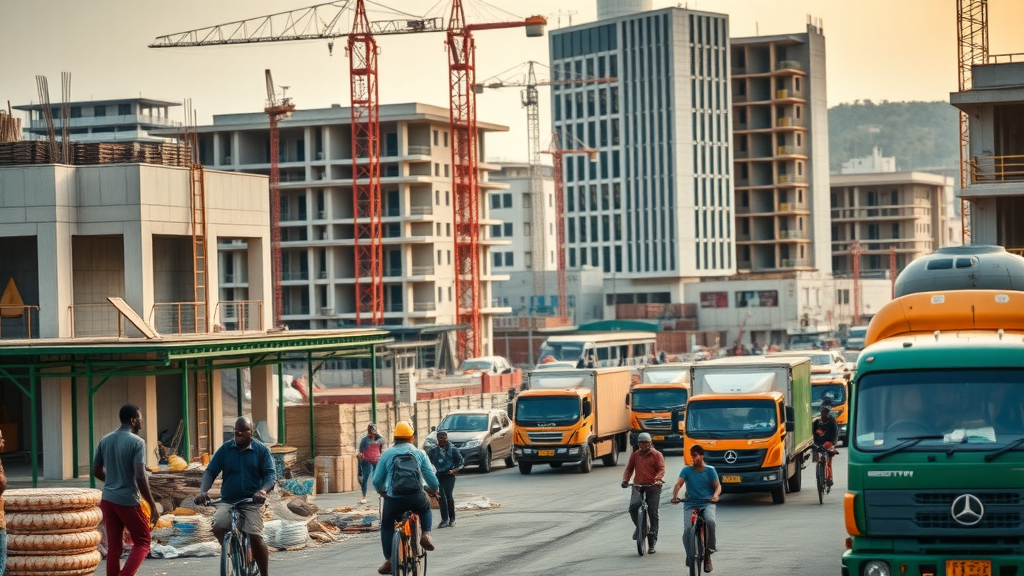

Policy Reforms and Trade Agreements
Reforming trade policies and establishing comprehensive trade agreements among African nations can stimulate economic growth and enhance cooperation. Streamlined regulations will encourage investment and foster a competitive trading environment.

People Also Ask
What is the meaning of intra-African trade?
Intra-African trade involves the exchange of goods and services among African countries, aiming to harness the continent's resources and potential for mutual economic benefit.
What is an example of an intra trade?
An example of intra-African trade could be the exchange of agricultural products between East African countries, facilitating regional self-sufficiency and economic stability.
What is the current intra-African trade?
The current state of intra-African trade is low compared to other regions, accounting for about 15% of total trade due to various barriers and inefficiencies.
Why is intra-African trade so low?
Intra-African trade remains low due to historical trade barriers, political instability, lack of infrastructure, and insufficient economic integration policies among member states.
Key Takeaways
- Intra-African trade is crucial for economic growth.
- FEDA plays a vital role in facilitating trade.
- Overcoming trade barriers is essential for progress.
Conclusion
In conclusion, intra-African trade is positioned as a pivotal component for achieving sustainable economic growth across the continent. As nations begin to recognize the importance of collaboration and integration, organizations like FEDA will continue to play a vital role in facilitating trade. With the right policies and investments, Africa's trade landscape is on the cusp of transformation.
Call to Action: Join the Conversation on Intra-African Trade
We invite you to engage with this topic by sharing your insights and experiences regarding intra-African trade. How can we collectively work towards fostering a more integrated and prosperous African economic landscape?
A video discussing the impact of intra-African trade on economic growth, featuring interviews with experts and case studies.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 





 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 

Write A Comment